Understanding and Managing Shoulder Internal Rotation Pain: A Comprehensive Guide

Shoulder internal rotation pain is a common complaint among individuals of varying ages and activity levels. Whether you're an athlete, a working professional, or someone experiencing discomfort with everyday movements, understanding the intricacies of shoulder internal rotation pain is essential for effective management and recovery. This in-depth guide delves into the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatments, and preventative measures related to shoulder internal rotation pain, empowering you with the knowledge to improve your shoulder health.
What is Shoulder Internal Rotation and Why Is It Important?
The shoulder joint, also known as the glenohumeral joint, is one of the most mobile and complex joints in the human body. It allows for a wide range of movements, including abduction, adduction, flexion, extension, and rotation. Internal rotation specifically refers to the movement where the arm rotates inward toward the body's midline. This motion is vital for various daily activities, such as reaching behind your back, tucking in a shirt, or playing sports like tennis, baseball, or swimming.
Proper shoulder internal rotation is essential for maintaining functional mobility, strength, and overall upper limb health. When this specific movement is impaired or causes pain, it can significantly diminish your quality of life and athletic performance.
Causes of Shoulder Internal Rotation Pain
The causes of shoulder internal rotation pain are diverse, ranging from acute injuries to chronic conditions. A comprehensive understanding of these causes is crucial for diagnosis and targeted treatment.
1. Rotator Cuff Injuries
The rotator cuff, composed of four muscles and their tendons, stabilizes the shoulder joint and facilitates rotation. Tears, tendinitis, or strain of these tendons can lead to pain during internal rotation movements. Common rotator cuff injuries include:
- Tendinitis or impingement syndrome
- Partial or full-thickness tears
- Rotator cuff tendinopathy
2. Shoulder Impingement Syndrome
This condition involves compression of shoulder tendons or bursae during movement, especially with repetitive internal rotation, leading to pain, inflammation, and restricted movement.
3. Labral Tears
The shoulder labrum is a ring of cartilage that deepens the glenoid cavity. Tears, especially those involving the anterior or posterior labrum, may cause pain during internal rotation and can be associated with shoulder instability.
4. Glenohumeral Osteoarthritis
C artik degeneration of the shoulder joint cartilage can cause pain, stiffness, and restricted movement, including internal rotation.
5. Biceps Tendinopathy
Inflammation or degeneration of the biceps brachii tendon can result in pain during internal rotation, especially if the biceps attach near the shoulder joint.
6. Muscle Strains and Overuse
Overuse or sudden overload of shoulder muscles, particularly during sports or repetitive tasks, can cause strains leading to pain.
7. Adhesive Capsulitis (Frozen Shoulder)
This condition involves stiffness and pain due to thickening and tightening of the shoulder capsule, often affecting internal rotation significantly.
Recognizing Symptoms of Shoulder Internal Rotation Pain
Symptoms associated with shoulder internal rotation pain can vary based on the underlying cause. Common signs include:
- Pain localized deep within or around the shoulder joint, often worsened during internal rotation or reaching behind your back
- Limited range of motion, especially in internal rotation and combined movements
- Weakness in the affected shoulder
- Swelling or tenderness over the joint
- Discomfort during specific activities like throwing, lifting, or pulling
- Clicking or catching sensations in the shoulder during movement
Diagnosing Shoulder Internal Rotation Pain
Accurate diagnosis is pivotal for effective treatment. Medical professionals will typically perform a comprehensive assessment, including:
- Detailed medical history to understand onset, duration, and aggravating factors
- Physical examination assessing active and passive range of motion
- Specific tests such as impingement signs, apprehension tests, and stability assessment
- Imaging studies like X-rays to evaluate bone integrity, MRI for soft tissue evaluation, and ultrasound for dynamic assessment
Effective Treatment Options for Shoulder Internal Rotation Pain
The approach to managing shoulder internal rotation pain depends on its etiology, severity, and patient-specific factors. The key goals are pain relief, restoring range of motion, and strengthening the shoulder muscles.
1. Conservative Management
Many cases respond well to non-invasive therapies, including:
- Rest and activity modification to prevent aggravation
- Ice application to reduce inflammation and swelling
- Physical therapy focusing on gentle stretching, strengthening, and mobility exercises tailored to your condition
- NSAIDs (Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs) for pain and inflammation control
- Postural correction to reduce undue stress on the shoulder
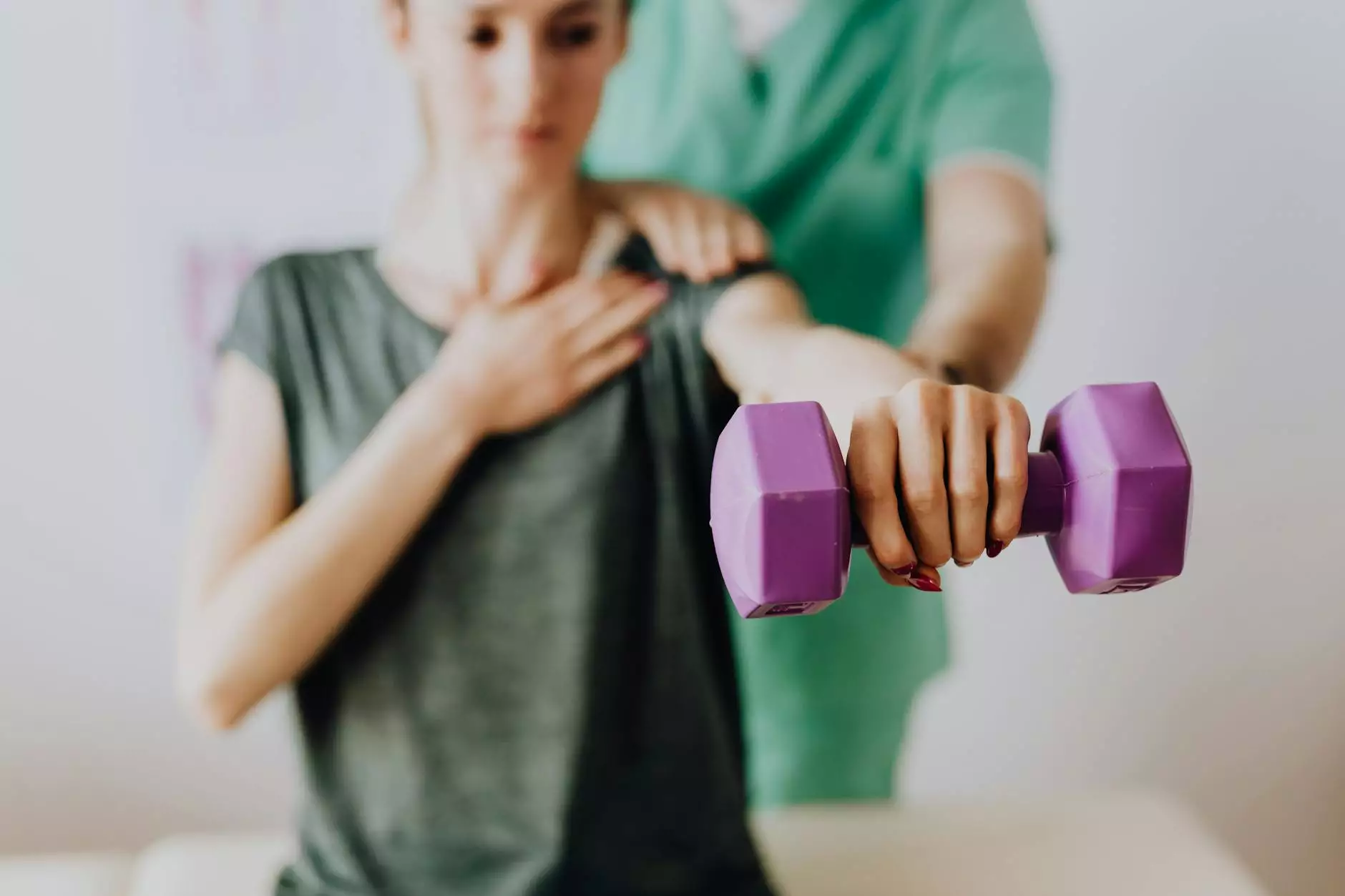
2. Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation
A customized physical therapy program is essential for restoring shoulder mobility and function. These programs often include:
- Stretching exercises targeting shoulder capsule tightness
- Strengthening exercises for rotator cuff and scapular stabilizers
- Manual therapy techniques to improve joint mobility
- Proprioceptive training to enhance joint position sense
- Gradual reintroduction of functional movements and sports-specific drills
3. Advanced Interventions
If conservative treatments fail or if structural issues are identified, more advanced options may include injections or surgical interventions:
- Corticosteroid injections to reduce inflammation and pain
- Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy to promote healing of damaged tissues
- Arthroscopic surgery for rotator cuff repairs, labral tears, or removal of impingement tissues
- Shoulder stabilization procedures for recurrent instability
Preventing Shoulder Internal Rotation Pain: Tips and Strategies
Prevention is always better than cure. Incorporating specific habits and exercises into your routine can help prevent shoulder internal rotation pain.
- Regular stretching of shoulder muscles, especially if you engage in repetitive or overhead activities
- Strengthening exercises for the rotator cuff and scapula to maintain muscular balance
- Proper ergonomics during work and daily activities to minimize shoulder strain
- Adequate warm-up and cool-down routines before sports or strenuous tasks
- Gradual progression in activity intensity and duration to prevent overuse injuries
- Maintaining good posture to reduce undue stress on the shoulder joint
The Role of Health & Medical Professionals in Shoulder Care
Consulting with qualified health and medical professionals ensures proper diagnosis and personalized treatment plans. At [iaom-us.com](https://iaom-us.com), specialists in chiropractic care, orthopedics, and physiotherapy collaborate to deliver optimal outcomes. They provide:
- Accurate diagnosis through advanced imaging and assessments
- Tailored rehabilitation programs
- Minimally invasive treatments when appropriate
- Preventive education to avoid future injuries
- Guidance on optimal lifestyle modifications for ongoing shoulder health
Conclusion: Empowering Your Shoulder Health
Achieving and maintaining healthy shoulder function is vital for overall well-being and active living. Understanding shoulder internal rotation pain—its causes, symptoms, and treatment options—empowers you to take proactive steps towards recovery. Whether through conservative management, physical therapy, or medical intervention, timely action can significantly reduce pain, restore mobility, and prevent future issues.
Remember, you don't have to endure shoulder pain silently. Early consultation with healthcare professionals, combined with a dedicated approach to rehabilitation and prevention, is your best strategy for long-term shoulder health. At iaom-us.com, our multidisciplinary team is committed to supporting you on your journey to pain-free, functional shoulders.